Future of Cybersecurity

Cybersecurity hacks can cause irreparable damage to individuals, businesses, and countries. According to a 2018 White House report, the Council of Economic Advisers estimates “malicious cyber activity cost the U.S. economy between $57 billion and $109 billion in 2016.” To combat this trend, in the coming years, private citizens, organizations, and governments will be increasingly investing in ways to improve their online security and prevent cyber attacks.
To learn more, check out the infographic below about online Cybersecurity.
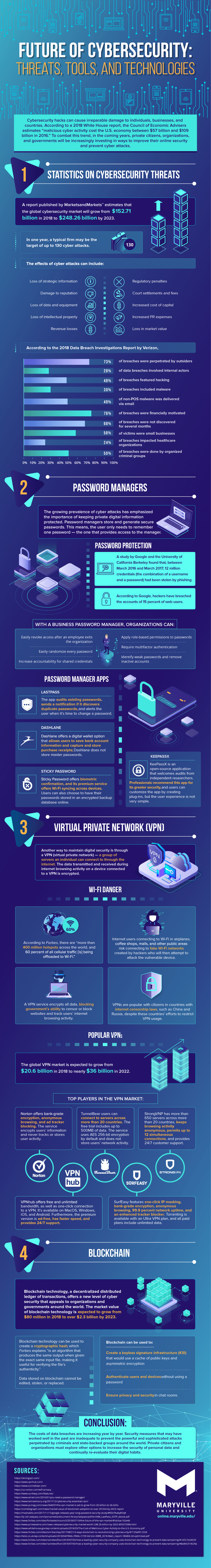
Statistics on Cybersecurity Treats
A report published by MarketsandMarkets™ estimates that the global cybersecurity market will grow from $152.71 billion in 2018 to $248.26 billion by 2023. In one year, a typical firm may be the target of up to 130 cyber attacks.
The effects of cyber attacks can be devastating. Fallout can include the loss of strategic information, damage to reputation, regulatory penalties, increased cost of capital and PR expenses, and loss in revenue and market value.
According to the 2018 Data Breach Investigation Report by Verizon, 73% of breaches were perpetrated by outsiders, and 28% involved internal actors. The report also found that 48% featured hacking, and 30% included malware. In the case of the latter, it was determined that 49% of non-POS malware was delivered via mail.
Furthermore, it was determined that 76% of breaches were financially motivated, and that 58% of breach victims were small businesses. It was also found that 68% of breaches went undetected for several months.
Password Managers
The growing prevalence of cyber attacks has emphasized the importance of keeping private digital information protected. Password managers tore and generate secure passwords. This means, the user only needs to remember one password – the one that provides access to the manager.
Password Protection
A study by Google and the University of California Berkeley found that, between March 2016 and March 2017, 12 million credentials (the combination of a username and a password) had been stolen by phishing. According to Google, hackers have breached the accounts of 15 percent of web users.
These stats highlight why a business password manager can be so important. With a business password manager, organizations can easily revoke access after an employee exits the company. They can also increase accountability for shared credentials. Additionally, they can easily randomize every password, identify weak passwords, and assign passwords role-based permissions. Finally, they can also put requirements concerning multifactor authentication in place.
Password Manager Apps
There are a few password manager apps on the market for businesses to choose from. Lastpass, Dashlane, Sticky Password, and Keepassx all offer various security services, although professionals recommend this latter app for its greater security capabilities.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Another way to maintain digital security is through a virtual private network, or VPN. This network is a group of services that an individual can connect to via the Internet. The data transmitted and received during internet browsing activity on a device connected to a VPN is encrypted.
Wi-Fi Danger
According to Forbes, there are “more than 400 million hotspots across the world, and 60 percent of all cellular traffic [is] being offloaded to Wi-Fi.” What’s more, Internet users connecting to Wi-Fi in airplanes, coffee shops, malls, and other public areas risk connecting to face Wi-Fi networks created by hackers who will then attempt to attack the vulnerable device.
However, a VPN service encrypts all data, blocking government’s ability to censor or block and track users’ Internet activity. Not surprisingly, VPNs are popular with citizens in countries with internet censorship laws, such as China and Russia, despite these countries’ efforts to restrict VPN usage. It’s no wonder that the global VPN market is poised to grow from $20.6 billion in 2018 to nearly $36 billion in 2022.
There are several key players in the VPN market. These include Norton, VPN hub, TunnelBear, SurfEasy, and StrongVNP. These services offer a wide range of features, including anonymous browsing, multi-server connections, and encryption.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology, a decentralized distributed ledger of transactions, offers a new level of cybersecurity that appeals to organizations and governments around the world. the market value of blockchain technology is expected to grow from $80 million in 2018 to over $2.3 billion by 2023.
Blockchain technology can be used to create a cryptographic hash, which Forbes explains “is an algorithm that produces the same output when given the exact same input file, making it useful for verifying the file’s authenticity.” Data stored on blockchain cannot be edited, stolen, or replaced. Blockchain can also be used to create a keyless signature infrastructure (KSI) that would use a cache of public keys and asymmetric encryption. They can also authenticate users and devices without using a password and can additionally ensure privacy and security in chat rooms.
Conclusion
The costs of data breaches are increasing annually. Security measures that may have worked well in the past are inadequate to prevent the powerful and sophisticated attacks perpetrated by criminals and state-backed groups around the world. Private citizens and organizations must explore other options to increase the security of personal data and continually re-evaluate their digital habits.

